Bio-integrative Orthopedic Bone Substitutes
Fully Resorbable Bone Substitutes with Structural Support
Ossiform® is developing a new generation of bio-integrative bone substitutes. The P3D Bone is printed with a tailored mix of cancellous and cortical bone-like components to facilitate fusion while meeting the specific structural demands of diversified applications. The result is a more natural implant in terms of both material, shape, and structure.
In preclinical studies, the P3D Bone demonstrates osteoconduction with a rapid formation of new vascularized bone, osseointegration with native bone, and a simultaneous and balanced bioresorption to ensure structural stability throughout the healing process.
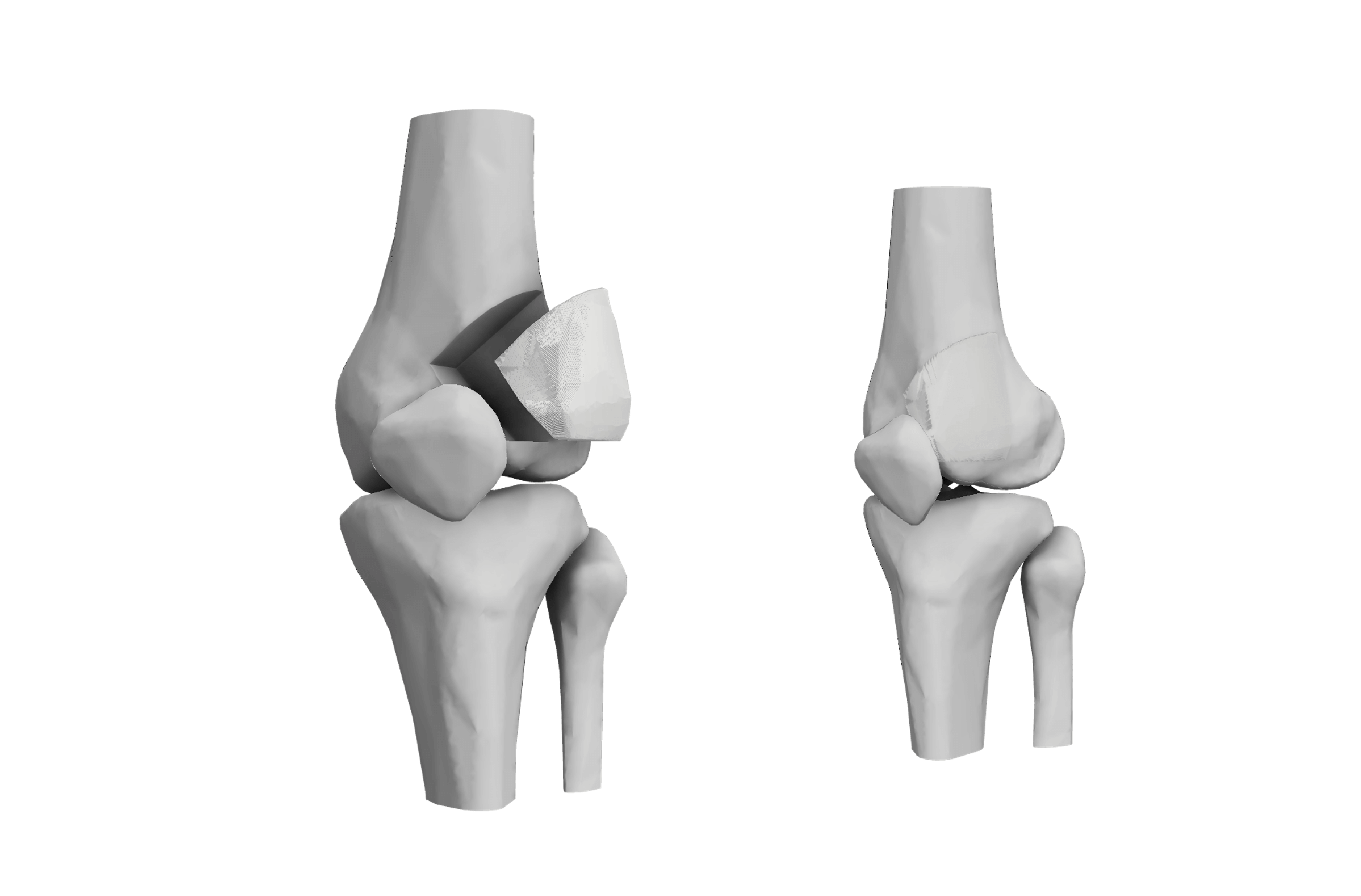
The P3D Bone illustrations shown on this site are intended to demonstrate potential use cases. Products are not cleared by the regulatory authorities and are therefore not approved for sale.
Tricalcium Phosphate: The Optimal Synthetic Choice
Over the past 40 years, bioceramic materials have proven very attractive bone graft substitutes, with beta-tricalcium phosphate (β-TCP) and hydroxyapatite (HA) being some of the most preferred due to their osteoconductive and osteoinductive properties.
While the two are sometimes mistaken for one another due to their chemical similarities, β-TCP has been proven to have superior properties compared to HA in terms of cell-mediated resorption and osteoconductivity. As a result, β-TCP has been widely used for filling and reconstructing bony defects in orthopedic surgery and spinal fusion.
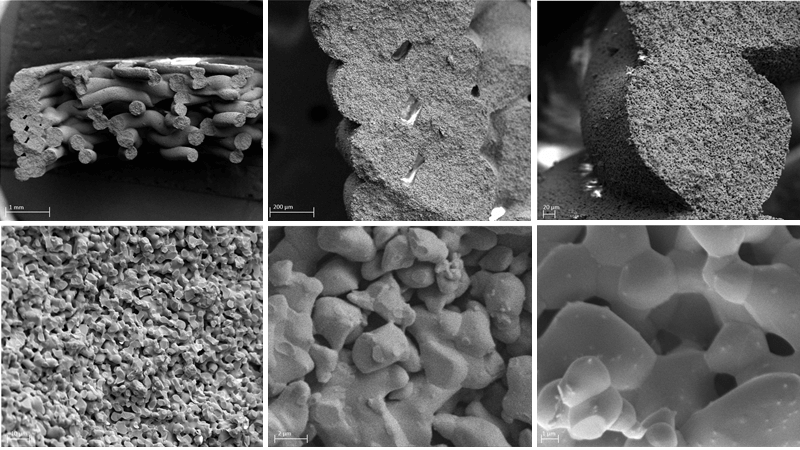
Furthermore, the resorption rate and mechanical properties of the β-TCP bone graft substitute can be controlled via its 3D printed design to ensure structural stability during bone healing.

Ossiform® developed a technology to give shape and structure to the well-recognized material β-TCP

01
Pure β-TCP
The material has been used clinically for the past 40 years, primarily in non-structural forms like paste, and is known to carry minimal risk of complications. Our bodies recognize it as bone, and it therefore completely remodels into natural bone over time.
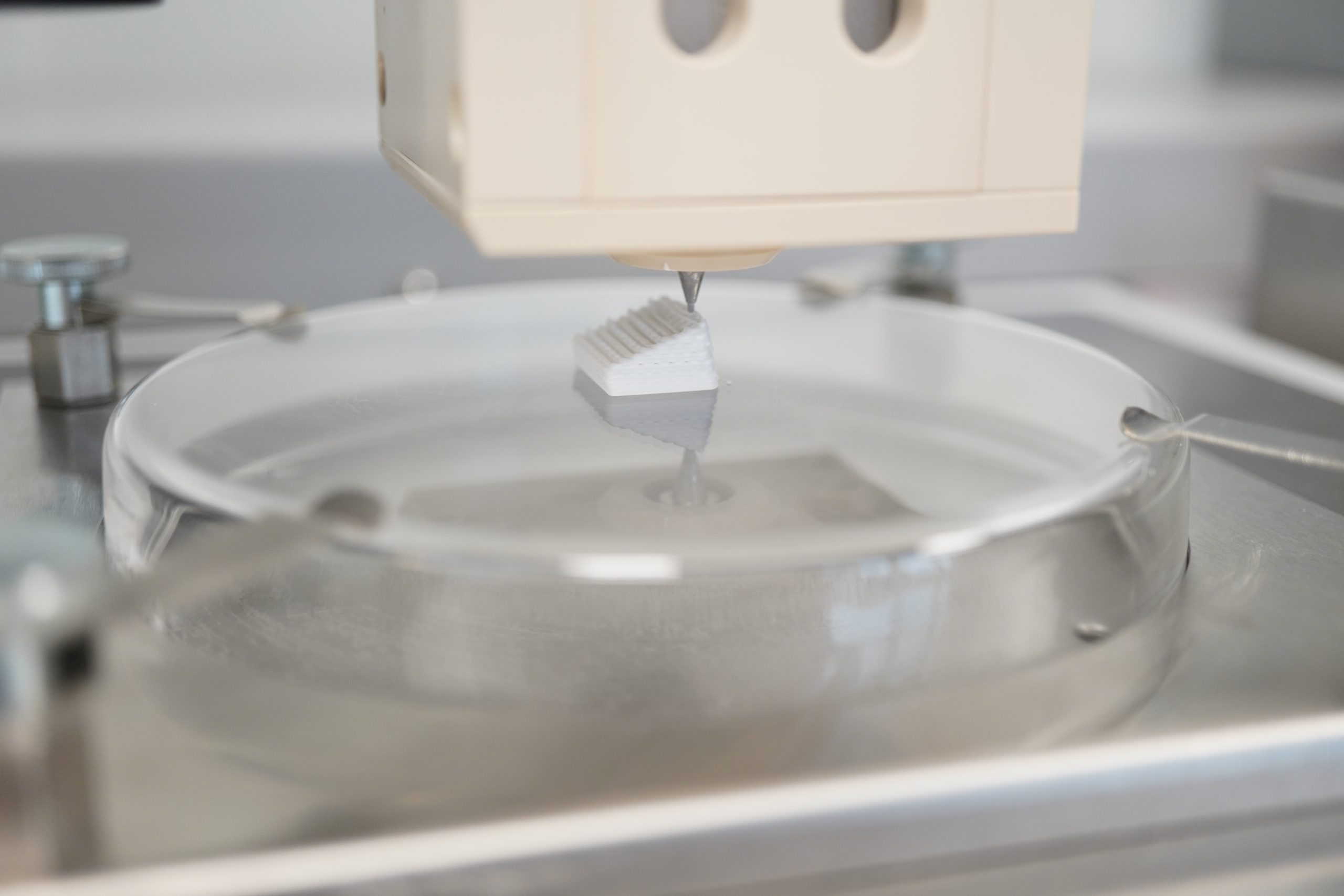

02
3D Printing
Ossiform® developed a 3D printing technique to give the material shape and structure, using 3D design to achieve ideal trade-offs between porosity and mechanical factors to match the specific demands of diversified applications in bone repair.
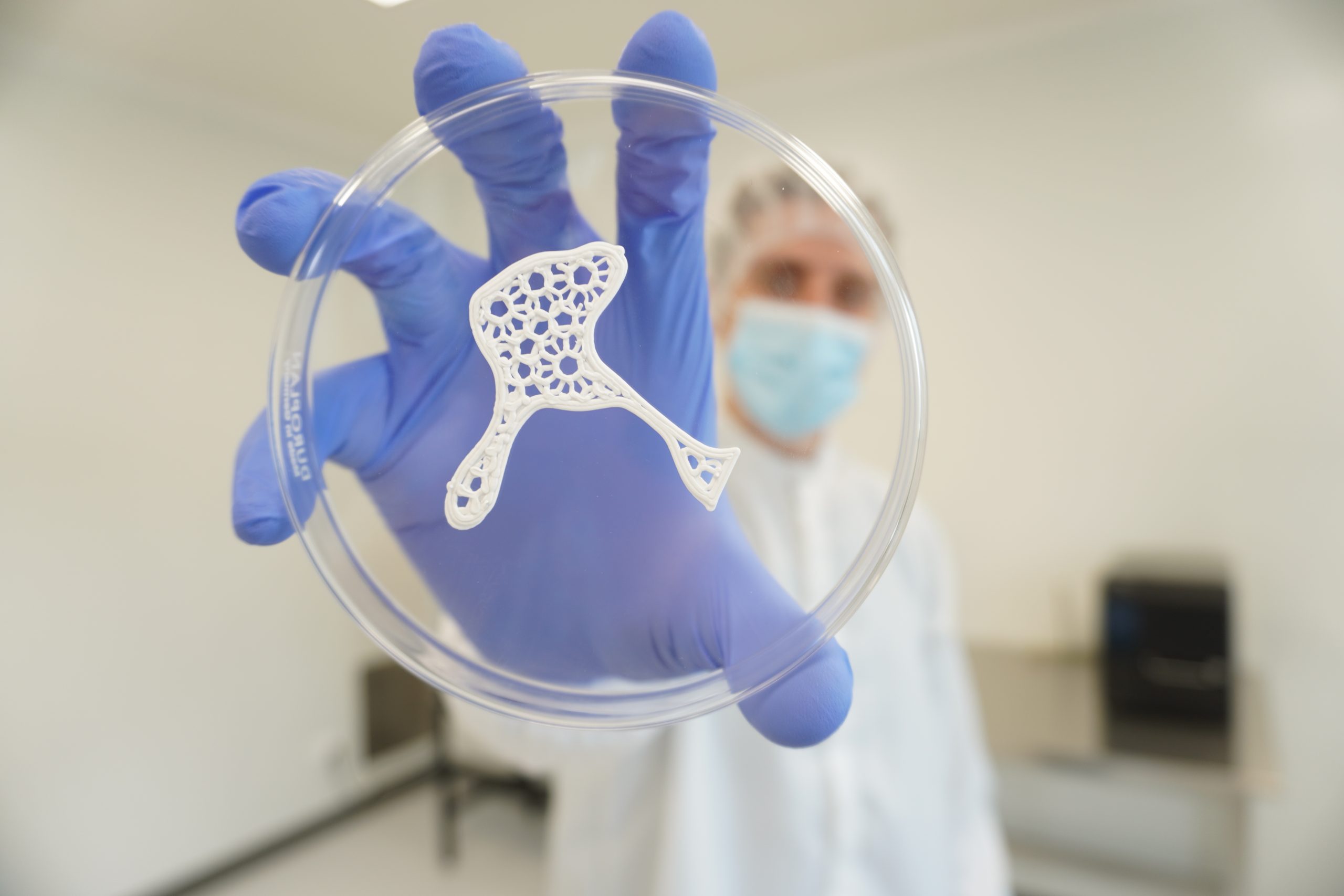

03
Structural implants
The P3D Bone provides a unique combination of natural and structural properties, thereby enabling metal-free solutions that surgeons can have confidence in, both in the short and long term, from anatomical fit to full fusion.
Fluid absorption
The porous β-TCP structure effectively wicks up fluids and is rapidly saturated throughout.
The video is a raw shot and has not been sped up.
If you cannot see this video, please update your Cookie Consent to accept ‘Marketing Cookies’.
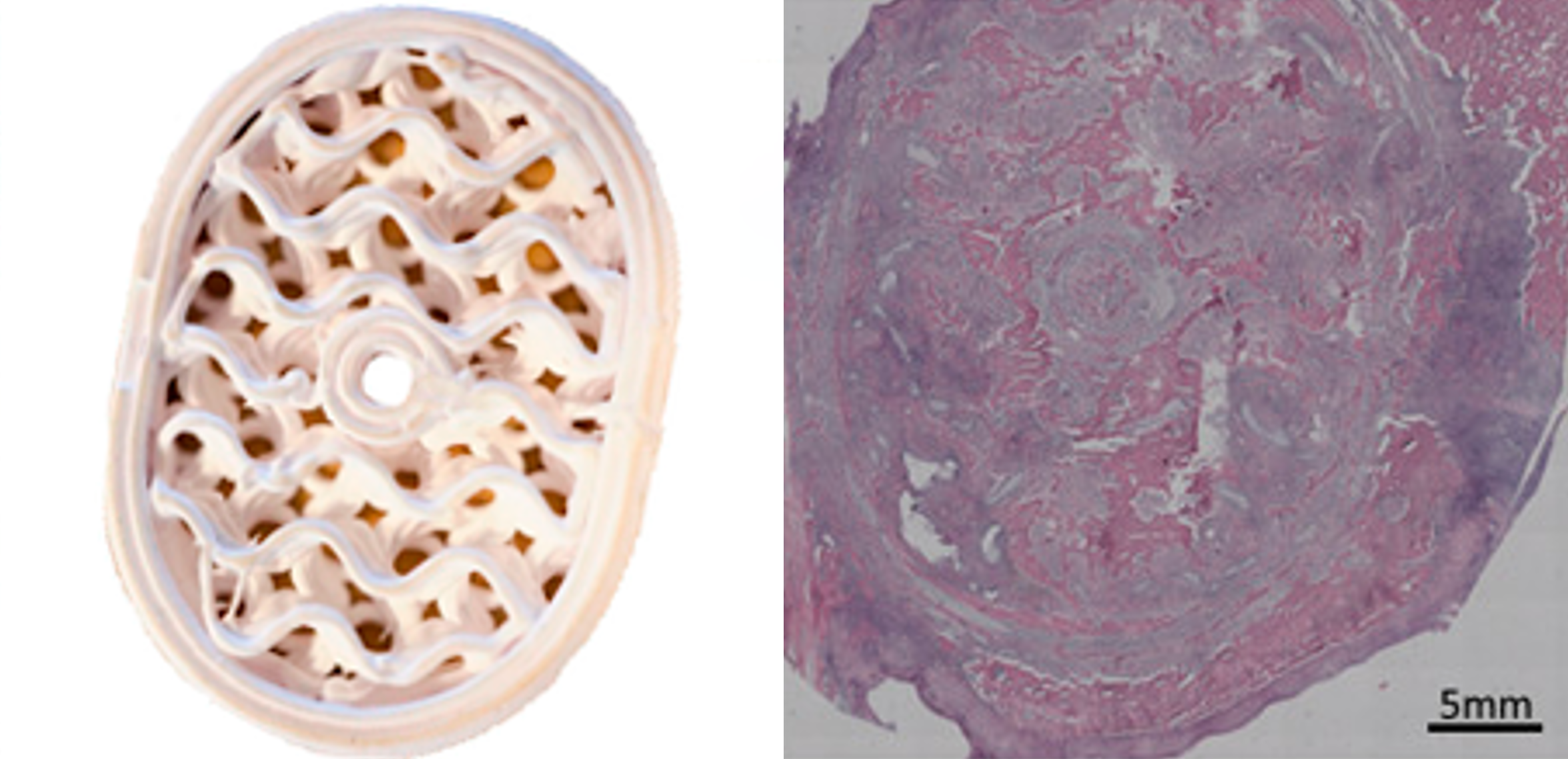
Preclinical data (Thygesen et al., 2022).
Structural ceramics – from anatomical fit to fusion
Ossiform’s structures are 3D printed with large interconnected macropores to enhance cell attachment, growth, and migration and enable vascularization throughout the entire bone graft substitute.
In preclinical studies, the porous structure, containing physiologically relevant micro- and macropores, enables a strong ongrowth and ingrowth of new native bone. Meanwhile, the bone-like chemical composition and structure provides ideal conditions for a simultaneous resorption of the bone graft substitute.
This process ensures an effective remodeling of the bone graft substitute into new vascularized bone.
Publications
Thygesen, T., et al. Comparison of off-the-shelf β-tricalcium phosphate implants with novel resorbable 3D printed implants in mandible ramus of pigs. Bone (2022): 116370.
Get access here
Jensen MB, et al. Treating mouse skull defects with 3D printed fatty acid and tricalcium phosphate implants. Journal of Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. (2020): 1-11
Get access here
Jensen MB, et al. Composites of fatty acids and ceramic powders are versatile biomaterials for personalized implants and controlled release of pharmaceuticals. Bioprinting 10 (2018): e00027
Get access here
Slots C, et al. Simple additive manufacturing of an osteoconductive ceramic using suspension melt extrusion. Dental Materials 33.2 (2017): 198-208.
Get access here
Sascha Senck, et al. Ceramic additive manufacturing and microstructural analysis of tricalcium phosphate implants using X-ray microcomputed tomography. Open Ceramics (2024): 100628.
Get access here


